Lead (Pb) Research: Scientific Publications
EPA researchers and their collaborators publish research results in a host of peer-reviewed scientific journals and reports. Below is a list of recent citations in the areas of:
- Blood Lead Level Modeling and Mapping
- Child and Adult Soil and Dust Ingestion Rates
- Lead and Drinking Water
- EPA and Cross-federal Agency Science Programs to Reduce Lead Exposure
Blood Lead Level Modeling and Mapping
Brown, J. S., Spalinger, S. M., Weppner, S. G., Hicks, K. J. W., Thorhaug, M., Thayer, W. C., Follansbee, M. H., & Diamond, G. L. (2023). Evaluation of the integrated exposure uptake biokinetic (IEUBK) model for lead in children. Journal of exposure science & environmental epidemiology, 10.1038/s41370-022-00473-2. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41370-022-00473-2
Brown, JS, Diamond, GL (2023). Derivation of first-order dissolution rates to estimate particle clearance and burden in the human respiratory tract. Particle and Fiber Tox 10: 17 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12989-023-00523-z
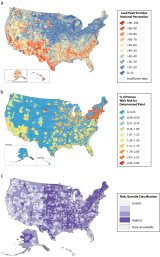
Stanek, L.W., Xue, J., Zartarian, V.G., Poulakos, A.G., Tornero-Velez, R., Snyder, E.G., Walts, A. and Triantafillou, K., (2024). Identification of high lead exposure locations in Ohio at the census tract scale using a generalizable geospatial hotspot approach. Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology, pp.1-9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41370-024-00666-x
Stanek, L., J. Xue, C. Lay, E. Helm, T. Speth, D. Lytle, M. Schock, and V. Zartarian. (2020). Modeled Impacts of Drinking Water Pb Reduction Scenarios on Children’s Exposures and Blood Lead Levels. Environmental Science & Technology, 54(15): 9474-9482. American Chemical Society, Washington, D.C.. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c00479.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (U.S. EPA) (2024). Technical Support Document for the All Ages Lead Model (AALM) version 3.0 – Parameters, Equations, and Evaluations. ORD, U.S. EPA, Washington, DC. EPA600/R‐23/346.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (U.S. EPA) (2024). Users Guide for the All Ages Lead Model (AALM) version 3.0 – Excel User Interface and Fortran Model Executable. ORD, U.S. EPA, Washington, DC. EPA600/B23/345.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (U.S. EPA) (2021). Advancing Pb Exposure and Biokinetic Modeling for U.S. EPA Regulatory Decisions and Site Assessments Using Bunker Hill Mining and Metallurgical Complex Superfund Site Data. U.S. EPA Office of Research and Development, Washington, DC, EPA/600/R-21/017F, 2021.
U.S. EPA. (2020). Integrated Exposure Uptake Biokinetic Model for Lead in Children (IEUBK), Version 2.0. https://www.epa.gov/superfund/lead-superfund-sites-software-and-users-manuals#guidance.
Ye, D., Brown, J. S., Umbach, D. M., Adams, J., Thayer, W., Follansbee, M. H., & Kirrane, E. F. (2022). Estimating the Effects of Soil Remediation on Children's Blood Lead near a Former Lead Smelter in Omaha, Nebraska, USA. Environmental health perspectives, 130(3), 37008. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP8657
Xue, J., Zartarian, V., Tornero-Velez, R., Stanek, L. W., Poulakos, A., Walts, A., Triantafillou, K., Suero, M., & Grokhowsky, N. (2022). A Generalizable Evaluated Approach, Applying Advanced Geospatial Statistical Methods, to Identify High Lead Exposure Locations at Census Tract Scale: Michigan Case Study. Environmental health perspectives, 130(7), 77004. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP9705
Zartarian, V, Poulakos, A, Garrison, VH, Spalt, N, Tornero-Velez, R, Xue, J, Egan, K, Courtney, J. (2022) Lead Data Mapping to Prioritize US Locations for Whole-of-Government Exposure Prevention Efforts: State of the Science, Federal Collaborations, and Remaining Challenges. American Journal of Public Health 112, S658_S669, https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2022.307051
Zartarian, V. G., Xue, J., Gibb-Snyder, E., Frank, J. J., Tornero-Velez, R., & Stanek, L. W. (2023). Children's lead exposure in the US: Application of a national-scale, probabilistic aggregate model with a focus on residential soil and dust lead (Pb) scenarios. Science of the Total Environment, 905, 167132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.167132
Zartarian, V.G., Xue, J., Poulakos, A.G., Tornero-Velez, R., Stanek, L.W., Snyder, E., Helms Garrison, V., Egan, K. and Courtney, J.G. (2024). A US lead exposure hotspots analysis. Environmental Science & Technology, 58(7), pp.3311-3321. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.3c07881
Zartarian VG, Xue J, Tornero-Velez R, Brown J. (2017). Children's Lead Exposure: A Multimedia Modeling Analysis to Guide Public Health Decision-Making. Environ Health Perspect. 125(9):097009. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP1605
Child and Adult Soil and Dust Ingestion Rates

Bosscher, V., D. Lytle, M. Schock, A. Porter, & M. Deltoral. (2019). POU Water Filters Effectively Reduce Lead in Drinking Water: A Demonstration Field Study in Flint, Michigan. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A, 54(5): 484-493. Taylor & Francis Group, London, UK. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2019.1611141.
Cohen, J., Hubbard, H., Özkaynak, H., Thomas, K., Phillips, L., & Tulve, N. (2024). Meta-analysis of soil and dust ingestion studies. Environmental Research, 261, 119649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2024.119649
DeSantis, M., Triantafyllidou, S., Schock, M., & Lytle, D.A. (2018). Mineralogical Evidence of Galvanic Corrosion in Drinking Water Lead Pipe Joints. Environmental Science & Technology, 52(6): 3365-3374.. American Chemical Society, Washington, D.C. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b06010.
DeSantis, M.S., Schock, M.R., Tully, J., and Bennett-Stamper, C. (2020). Orthophosphate Interactions with Destabilized PbO2 Scales. Environmental Science & Technology, 54(22): 14302-14311. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c03027.
Doré, E., D. Lytle, L. Wasserstrom, J. Swertfeger, and S. Triantafyllidou. (2020). Field Analyzers for Lead Quantification in Drinking Water Samples. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 50(20): 1-31. CRC Press LLC, Boca Raton, FL. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2020.1782654.
EPA STAR Grants: Estimating Children’s Soil and Dust Ingestion Rates for Exposure Science. https://www.epa.gov/newsreleases/epa-awards-over-9-million-research-better-understand-exposure-young-children-chemicals
Hubbard, H., Özkaynak, H., Glen, G., Cohen, J., Thomas, K., Phillips, L., & Tulve, N. (2022). Model-based predictions of soil and dust ingestion rates for U.S. adults using the stochastic human exposure and dose simulation soil and dust model. The Science of the total environment, 846, 157501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157501
Lytle, D., Schock, M, Formal, C., Bennett-Stamper, C., Harmon, S., Nadagouda, M., Williams, D., DeSantis, M., Tully, J., and Pham, M. (2020). Lead Particles Size Fractionation and Identification in Newark, New Jersey's Drinking Water. Environmental Science & Technology, 54(21): 13672-13679. American Chemical Society, Washington, D.C. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c03797.
Lytle, D., M. Schock, K. Wait, K. Cahalan, V. Bosscher, A. Porter, and M. Deltoral. (2019). Sequential Drinking Water Sampling as a Tool for Evaluating Lead in Flint, Michigan. Water Research, 157: 40-54. Elsevier Science Ltd., New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.03.042.
Lytle, D.A., Schock, M.R., & Triantafyllidou, S. (2018). Identify lead plumbing sources to protect public health. Opflow, 44(3): 16-20. https://doi.org/10.5991/OPF.2018.44.0027.
Muhlen, C., L. Voutsikakis, R. Murray, and J. Tully. (2020). Technical Support Summary, Water Infrastructure Division, Fiscal Year 2019. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, D.C., EPA/600/R-20/328.
Özkaynak, H., Glen, G., Cohen, J., Hubbard, H., Thomas, K., Phillips, L., & Tulve, N. (2022). Model based prediction of age-specific soil and dust ingestion rates for children. Journal of exposure science & environmental epidemiology, 32(3), 472–480. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41370-021-00406-5
Triantafyllidou, S., Wasserstrom, L., Nelson, J., Webb, D., Formal, C., Doré, E., and Lytle, D. (2023). Lead in synthetic and municipal drinking water varies by field versus laboratory analysis. Sci Total Environ., 891: 163873. Epub 2023 May 23. PMID: 37230337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.163873.
Tully, J., M. DeSantis, and M. Schock. (2019). Water quality-pipe deposit relationships in Midwestern lead pipes. Journal of the American Water Works Association, 1(2): 1-18. American Water Works Association, Denver, CO. https://awwa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/aws2.1127.
Williams, D., Parrett, C., Schock, M., Muhlen, C., Donnelly, P., and Lytle, D. (2018). Design and Testing of USEPA’s Flint Pipe Rig for Corrosion Control Evaluation. Journal of the American Water Works Association, 110(10): E16-E37. American Water Works Association, Denver, CO. https://doi.org/10.1002/awwa.1127.
Xing, W., E. Cao, K. Scheckel, X. Bai, and L. Li. (2018). Influence of phosphate amendment and zinc foliar application on heavy metal accumulation in wheat and on soil extractability impacted by a lead-smelter near Jiyuan, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(31): 31396-31406. Ecomed Verlagsgesellschaft AG, Landsberg, Germany. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3126-4.
Xing, W., Y. Zheng, K. Scheckel, Y. Luo, and L. Li. (2019). Spatial distribution of smelter emission heavy metals on farmland soil. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(2): 115. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7254-1.
Lead and Drinking Water

Bradham, K.D., Nelson, C.M., Sowers, T.D. et al (2023). A national survey of lead and other metal(loids) in residential drinking water in the United States. Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology (2023) 33:160–167; https://doi.org/10.1038/s41370-022-00461-6
Burkhardt, JB, Woo, H, Mason, J, Shang, F, Triantafyllidou, S, Schock, MR, Lytle, D, Murray, R (2022). Closure to “Framework for Modeling Lead in Premise Plumbing Systems Using EPANET” J Water Resources 148(2) https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0001304
Devine, C., Garcia-Bakarich, L., Platten, W., Jajeh, K., & Triantafyllidou, S. (2024). Review of historical plumbing codes for lead service line inventories in the United States. Water Practice & Technology, https://doi.org/10.2166/wpt.2024.212.
Devine, C., K. Mello, M. Desantis, M. Schock, J. Tully, and M. Edwards (2024). Calcium Phosphate Precipitation as an Unintended Consequence of Phosphate Dosing to High-pH Water. Environmental Engineering Science. Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., Larchmont, NY, 41(5):171-179, (2024). https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2023.0190
Devine, C., Triantafyllidou, S. A Literature Review of Bench Top and Pilot Lead Corrosion Assessment Studies. AWWA Water Science. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, NJ, 5(2):e1324, (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/aws2.1324
Doré, E, Formal, C, Muhlen, C, Williams, D, Harmon, S, Pham, M, Triantafyllidou, S, Lytle, DA. (2021). Effectiveness of point-of-use and pitcher filters at removing lead phosphate nanoparticles from drinking water. Water Res. Aug 1; 201: 117285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2021.117285
EPA 2023. Water filter effectiveness study, Benton Harbor, MI. https://www.epa.gov/mi/benton-harbor-michigan-drinking-water-study-results
Harmon SM, Tully J, DeSantis MK, Schock MR, Triantafyllidou S, Lytle DA (2022). A holistic approach to lead pipe scale analysis: Importance, methodology, and limitations. AWWA Water Sci. 4(2):0. https://doi.org/10.1002/aws2.1278
Hensley, K, Bosscher, V, Triantafyllidou, S, Lytle DA. (2021). Lead service line identification: A review of strategies and approaches AWWA Wat Sci https://doi.org/10.1002/aws2.1226
Liggett, J., Baribeau, H, Deshommes, E, Lytle, D, Masters, S, Muylwyk, Q, and Triantafyllidou, S. (2022). Service Line Material Identification: Experiences from North American Water Systems. Journal AWWA. American Water Works Association, Denver, CO, 114(1):8-19. https://doi.org/10.1002/awwa.1841
Schock MR, Lytle DA, James RR, Lal V, Tang M. (2021). Rapid and simple lead service line detection screening protocol using water sampling. AWWA Water Sci. 3(5):1-1255. https://doi.org/10.1002/aws2.1255
Smart, P., McRae, L., Formal, C., & Lytle, D. A. (2023). Development and optimization of a systematic approach to identifying lead service lines: One community's success. Water Research, 246, 120725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2023.120725
Tang, M., Lytle, D., Achtemeier, R., & Tully, J. (2023). Reviewing performance of NSF/ANSI 53 certified water filters for lead removal. Water Research, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2023.120425
Triantafyllidou S, Burkhardt J, Tully J, Cahalan K, DeSantis M, Lytle D, Schock M (2021). Variability and sampling of lead (Pb) in drinking water: Assessing potential human exposure depends on the sampling protocol. Environ Int.146:106259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.106259
Triantafyllidou, S., Wasserstrom, L., Nelson, J., Webb, D., Formal, C., Doré, E., & Lytle, D. (2023). Lead in synthetic and municipal drinking water varies by field versus laboratory analysis. Science of The Total Environment, 891, 163873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.163873
Tully, J., Schock, M., Shilling, S., Bosscher, V., Lytle, D., Harmon, S., & Bennett-Stamper, C. (2024). An evaluation of properly operated NSF/ANSI-53 Pb certified drinking water filters in Benton Harbor, MI. Journal of water and health, 22(2), 296-308. https://doi.org/10.2166/wh.2024.231
Zhang, Y., Wan, Y., Zheng, Y., Yang, Y., Huang, J., Chen, H., Chen, J., Mosa, A., & Gao, B. (2024). Hydrochar Loaded with Nitrogen-Containing Functional Groups for Versatile Removal of Cationic and Anionic Dyes and Aqueous Heavy Metals. Water, 16(23), 3387. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16233387
Lead and Soil

Alankarage, D., Betts, A., Scheckel, K. G., Herde, C., Cavallaro, M., & Juhasz, A. L. (2024). Remediation options to reduce bioaccessible and bioavailable lead and arsenic at a smelter impacted site-consideration of treatment efficacy. Environmental Pollution, 341, 122881.
Bradham, K., G. Diamond, C. Nelson, M. Noerpel, K. Scheckel, B. Elek, R. Chaney, Q. Ma, and D. Thomas. (2018). Long-Term in Situ Reduction in Soil Lead Bioavailability Measured in a Mouse Model. Environmental Science & Technology, 52(23): 13908-13913. American Chemical Society, Washington, D.C. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b04684.
Bradham, K.D., Nelson, C.M., Diamond, G.L., Thayer, W.C., Scheckel, K.G., Noerpel, M., Herbin-Davis, K., Elek, B., and Thomas, D.J. (2019). Dietary Lead and Phosphate Interactions Affect Oral Bioavailability of Soil Lead in the Mouse. Environ Sci Technol., 53(21): 12556-12564.Epub 2019 Oct 16. PMID: 31557437; PMCID: PMC8188726. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b02803.
George, S., J. James, R. Devereux, Y. Wan, G. Diamond, K. Bradham, K. Scheckel, and D. Thomas (2022). Ingestion of Remediated Lead-Contaminated Soils Affects the Fecal Microbiome of Mice. SCIENCE OF THE TOTAL ENVIRONMENT. Elsevier BV, AMSTERDAM, Netherlands, 837:155797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155797
George, SE, and Wan, Y. (2019). Advances in characterizing microbial community change and resistance upon exposure to lead contamination: Implications for ecological risk assessment. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 50(21): 2223-2270. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2019.1698260.
Griggs JL, Thomas DJ, Fry R, Bradham KD. (2021). Improving the predictive value of bioaccessibility assays and their use to provide mechanistic insights into bioavailability for toxic metals/metalloids - A research prospectus. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 24(7):307-324. doi:10.1080/10937404.2021.1934764
Hettiarachchi, G. M., Betts, A. R., Wekumbura, W. C., Lake, L., Mayer, M. M., Scheckel, K. G., & Basta, N. T. (2024). Lead: The most extensively spread toxic environmental contaminant. In Inorganic contaminants and radionuclides (pp. 113-150). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-90400-1.00006-9
Karna, R. R., Noerpel, M. R., Nelson, C., Elek, B., Herbin-Davis, K., Diamond, G., Bradham, K., Thomas, D. J., & Scheckel, K. G. (2020). Bioavailable soil Pb minimized by in situ transformation to plumbojarosite. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 118(3), e2020315117. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2020315117
Ippolito, J., L. Cui, J. Novak, and Mark G. Johnson (2019). Chapter 5 - Biochar for Mine Land Reclamation. Biochar from Biomass and Waste: Fundamentals and Applications, 75-90. Elsevier Inc, Waltham, MA.
Karna, R., Noerpel, M., Luxton, T., and Scheckel, K. (2018). Point of Zero Charge: Role in Pyromorphite Formation and Bioaccessibility of Lead and Arsenic in Phosphate-Amended Soils. Soil Systems, 2(2): 22. MDPI AG, Basel, Switzerland. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems2020022.
Kastury, F., Besedin, J., Betts, A.R., Asamoah, R., Herde, C., Netherway, P., Tully, J., Scheckel, K.G. and Juhasz, A.L. (2024). Arsenic, cadmium, lead, antimony bioaccessibility and relative bioavailability in legacy gold mining waste. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 469, p.133948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.133948
Kastury, F., Li, H., Karna, R., Betts, A., Scheckel, K.G., Ma, L.Q., Sowers, T.D., Bradham, K.D., Hettiarachchi, G.M. and Juhasz, A.L. (2023). Opportunities and challenges associated with bioavailability-based remediation strategies for lead-contaminated soil with arsenic as a Co-Contaminant—a critical review. Current Pollution Reports, 9(2), pp.213-225. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s40726-023-00252-z
Kastury, F., Placitu, S., Boland, J., Karna, R., Scheckel, K.G., Smith, E., and Juhasz, A. (2019). Relationship between Pb relative bioavailability and bioaccessibility in phosphate amended soil: Uncertainty associated with predicting Pb immobilization efficacy using in vitro assays. Environment International, 131: 104967. Elsevier, B.V., Amsterdam, Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.104967.
Kastury, F., Smith, E., Doelsch, E., Lombi, E., Donnelley, M., Cmielewski, P.L., Parsons, D.W., Scheckel, K.G., Paterson, D., de Jonge, M.D., Herde, C., and Juhasz, A.L. (2019). In Vitro, in Vivo, and Spectroscopic Assessment of Lead Exposure Reduction via Ingestion and Inhalation Pathways Using Phosphate and Iron Amendments. Environ Sci Technol., 53(17): 10329-10341. Epub 2019 Aug 13. PMID: 31356748; PMCID: PMC7436645. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b02448.
Kastury, F., E. Smith, E. Lombi, M. Donnelley, P. Cmielewski, D. Parsons, M. Noerpel, Kirk G. Scheckel, A. Kingston, G. Myers, D. Paterson, M. de Jonge, and A. Juhasz. (2019). Dynamics of Lead Bioavailability and Speciation in Indoor Dust and X-ray Spectroscopic Investigation of the Link between Ingestion and Inhalation Pathways. Environmental Science & Technology, 53(19): 11486-11495. American Chemical Society, Washington, D.C. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b03249.
Kastury, F., Smith, E., Karna, R. R., Scheckel, K. G., and Juhasz, A. L. (2018). Methodological factors influencing inhalation bioaccessibility of metal (loid)s in PM2.5 using simulated lung fluid. Environmental pollution, 241: 930-937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.05.094.
Kastury, F., E. Smith, E. Lombi, M. Donnelley, P. Cmielewski, D. Parsons, M. Noerpel, Kirk G. Scheckel, A. Kingston, G. Myers, D. Paterson, M. de Jonge, and A. Juhasz. (2019). Dynamics of Lead Bioavailability and Speciation in Indoor Dust and X-ray Spectroscopic Investigation of the Link between Ingestion and Inhalation Pathways. Environmental Science & Technology, 53(19): 11486-11495.. American Chemical Society, Washington, D.C. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b03249.
Misenheimer, J., Nelson, C., Huertas, E., Medina-Vera, M., Prevatte, A., and Bradham, K. (2018). Total and bioaccessible soil arsenic and lead levels and plant uptake in three urban community gardens in Puerto Rico. Geosciences, 8(2): 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8020043.
Noerpel M., Pribil, M.J., Rutherford, D.L., Law, P., Karen, D., Bradham, K.D., Nelson, C.M., Weber, R., Gunn, G., Scheckel, K.G. (2020). Lead speciation, bioaccessibility and source attribution in Missouri’s Big River Watershed. Applied Geochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2020.104757.
Plunkett, SA, Eckley, CS, Luxton, TP, Johnson, MG (2022). The effects of biochar and redox conditions on soil Pb bioaccessibility to people and waterfowl, Chemosphere, Volume 294, 2022, 133675, ISSN 0045-6535, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.133675.
Scheckel, K.G., Karna, R.R., Partridge, C.R., Bradham, K.D., Thomas, D.J., Noerpel, M.R., Goetz, J.L., Luxton, T.P., and Sowers, T.D. (2022). Method for sequestering ions in an environmental matrix. U.S. Patent no. 20220355353.
Sowers, T. D., Blackmon, M. D., Betts, A. R., Jerden, M. L., Scheckel, K. G., & Bradham, K. D. (2023). Potassium jarosite seeding of soils decreases lead and arsenic bioaccessibility: A path toward concomitant remediation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 120(50), e2311564120. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2311564120
Sowers, T. D., Blackmon, M. D., Wilkin, R. T., Rovero, M., Bone, S. E., Jerden, M. L., ... & Bradham, K. D. (2024). Lead Speciation, Bioaccessibility, and Sources for a Contaminated Subset of House Dust and Soils Collected from Similar United States Residences. Environmental Science & Technology. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.4c01594
Sowers T.D., Blackmon, M.D., Bone, S.E., Kirby, A.M., Jerden, M.L., Noerpel, M.R., Scheckel, K.G., and Bradham, K.D. (2022). Successful Conversion of Pb-Contaminated Soils to Low-Bioaccessibility Plumbojarosite Using Potassium-Jarosite at Ambient Temperature. Environ Sci Technol., 56(22): 15718-15727. Epub 2022 Oct 14. PMID: 36239028; PMCID: PMC10398550. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.2c05606.
Sowers, T. D., Bone, S. E., Noerpel, M. R., Blackmon, M. D., Karna, R. R., Scheckel, K. G., Juhasz, A. L., Diamond, G. L., Thomas, D. J., & Bradham, K. D. (2021). Plumbojarosite Remediation of Soil Affects Lead Speciation and Elemental Interactions in Soil and in Mice Tissues. Environmental science & technology, 55(23), 15950–15960. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c06067
Sowers, T.D., Nelson, C.M., Blackmon, M.D., Li, K., Jerden, M.L., Kirby, A.M., Kovalcik, K., Cox, D., Dewalt, G., Friedman, W. and Pinzer, E.A. (2024). United States house dust Pb concentrations are influenced by soil, paint, and house age: insights from a national survey. Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology, pp.1-9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41370-024-00655-0
Tucillo, ME, Blue, J, Koplos, J, Kelly, J, Wilkin, RT (2023). Complexities in attributing lead contamination to specific sources in an industrial area of Philadelphia, PA. Heliyon https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15666
Wan, Y, Devereux, R, George, SE, Chen, J, Gao, B, Noerpel, M, Scheckel, K (2022). Interactive effects of biochar amendment and lead toxicity on soil microbial community, Journal of Hazardous Materials, Volume 425,2022,127921,ISSN 0304-3894, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127921.
EPA and Cross-federal Agency Science Programs to Reduce Lead Exposure

Aurell, J., Holder, A., Gullett, B., McNesby, K., and Weinstein, J. (2019). Characterization of M4 Carbine Rifle Emissions With Three Ammunition Types. Environmental Pollution, 254(A): 112982. Elsevier Science Ltd., New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.112982.
Axelrad, D.A., Coffman, E., Kirrane, E.F., and Klemick, H. (2022). The relationship between childhood blood lead levels below 5 µg/dL and childhood intelligence quotient (IQ): Protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ Int., 169: 107475. Epub 2022 Aug 30. PMID: 36162279; PMCID: PMC9896788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2022.107475
Breysse, P, Cascio, W, Geller, AM, Choiniere, C, Ammon, M. (2022). Targeting Coordinated Federal Efforts to Address Persistent Hazardous Exposures to Lead. American Journal of Public Health 112, S640_S646, https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2022.306972
Frank, J., A. Poulakos, R. Tornero-Velez, and J. Xue. (2019). Systematic review and meta-analyses of lead (Pb) concentrations in environmental media (soil, dust, water, food, and air) reported in the United States from 1996 to 2016. Science of the Total Environment, 694: 133489. Elsevier B.V., Amsterdam, Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.295.
Geller, AM. (2022). Science and science-based tools to address persistent hazardous exposures to lead. J Env Health, Volume 85, Number 5 (Dec 2022) https://www.neha.org/current-issue
Nilsen, F., and Tulve, N. (2020). A systematic review and meta-analysis examining the interrelationships between chemical and non-chemical stressors and inherent characteristics in children with ADHD. Environmental Research, 180: 108884. . Elsevier B.V., Amsterdam, Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.108884.
Shaffer, R.M., Forsyth, J.E., Ferraro, G., Till, C., Carlson, L.M., Hester, K., Haddock, A., Strawbridge, J., Lanfear, C.C., Hu, H., and Kirrane, E. (2022). Lead exposure and antisocial behavior: A systematic review protocol. Environ Int., 168: 107438. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 35994796.
Stanek, L.W., Grokhowsky, N., George, B.J., and Thomas, K.W. (2023). Assessing lead exposure in U.S. pregnant women using biological and residential measurements. Sci Total Environ. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 37739076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.167135.
U.S. EPA. (2023). Integrated Science Assessment (ISA) for Lead (Pb) (External Review Draft). U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, D.C. EPA/600/R 23/061. https://www.epa.gov/isa/integrated-science-assessment-isa-lead.