GHGRP and the Oil and Gas Industry
The petroleum and natural gas (“oil and gas”) industry includes a wide range of operations and equipment, including wells, natural gas gathering lines and processing facilities, storage tanks, and transmission and distribution pipelines. The oil and gas industry is the largest industrial source of methane emissions in the United States. Methane is a potent GHG with a global warming potential more than 25 times that of carbon dioxide, and is responsible for approximately one-third of current warming from human activities.
Relevant GHGRP Subparts
The GHGRP specifies reporting requirements for a wide range of emission sources and entities across the oil and gas industry. It requires affected owners or operators to collect GHG data, calculate GHG emissions, and follow the specified procedures for quality assurance, missing data, recordkeeping, and reporting.
Subpart W – Petroleum and Natural Gas Systems
Subpart W applies to any facility that contains petroleum and natural gas systems and that emits 25,000 mt CO2e or more per year. Petroleum and natural gas systems are defined by the GHGRP as facilities that participate in production, processing, compression, gathering and boosting, storage, transmission, and distribution.
Reporter Resources
Data Resources
- View the GHGRP Oil and Gas Dashboard.
- View StoryMaps about the onshore wells and GHGRP.
- View emissions data grouped by Subpart W industry segment and emission source.
Subpart Y – Petroleum Refineries
Subpart Y applies to any facility that refines petroleum and meets the source category definition. This subpart does not specify a minimum level of emissions (or “threshold”) reporting requirement, so it applies to all petroleum refineries.
Subpart MM – Suppliers of Petroleum Products
Subpart MM applies to all petroleum refineries and to importers and exporters of petroleum products and natural gas liquids whose supplied products would result in 25,000 metric tons CO2e or more per year if the products were fully combusted.
Subpart NN – Suppliers of Natural Gas and Natural Gas Liquids
Subpart NN applies to all fractionators of natural gas liquids and to natural gas distribution companies that deliver 460,000 Mscf or more of natural gas per year. Facilities subject to Subpart NN requirements must report the emissions that would result from the complete combustion or oxidation of the products that they sell.
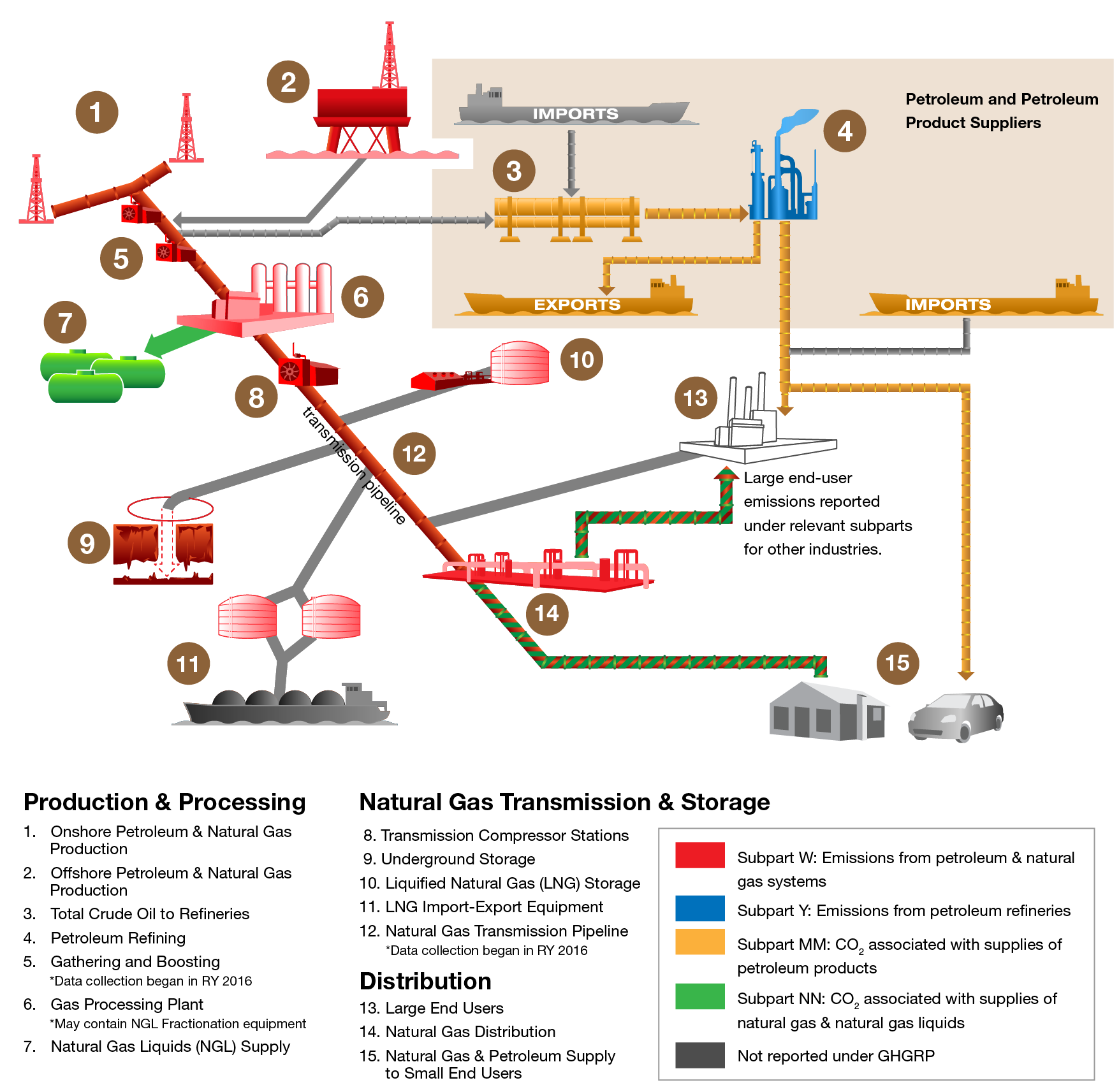
Oil and Gas Industry Overview Diagram
The GHGRP covers emissions from different aspects of the oil and gas industry through several of its subparts. Click on a number in the diagram below to find out how the GHGRP addresses emissions from different phases of oil and gas extraction, production, transport, and use by collecting information from the four subparts described above.
| Legend # | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Each owner or operator of onshore petroleum and natural gas production wells and related equipment reports under subpart W the combined emissions for all wells that they own or operate within each hydrocarbon basin. Emissions from stationary and portable fuel combustion equipment are reported under "Subpart W" of the GHGRP. Learn more about emissions from this source. |
| 2 | Emissions from offshore petroleum and natural gas production are reported under Subpart W of the GHGRP for each platform. These facilities also report emissions from fossil fuel combustion under Subpart C. Learn more about emissions from this source. |
| 3 | Each refinery reports all of the crude oil, natural gas liquids, and bulk petroleum products that enter the refinery for processing or other use. |
| 4 | Each refinery reports direct emissions from refinery specific processes under Subpart Y of the GHGRP and emissions from fossil fuel combustion under Subpart C. Some refineries also report emissions from other sources such as hydrogen production (Subpart P), petrochemical production (Subpart X) and industrial waste landfills (Subpart TT). Learn more about emissions from this source. Petroleum product suppliers. Refineries and importers/exporters of petroleum products report as a supplier of petroleum products under Subpart MM of the GHGRP. These suppliers do not report direct emissions under Subpart MM, but instead report the quantity of CO2 that would be emitted if the fuels that they produce, import, or export each year were combusted, released to the atmosphere, or oxidized. Learn more about reported CO2 from this source. |
| 5 | Onshore petroleum and natural gas gathering and boosting means gathering pipelines and other equipment used to collect petroleum and/or natural gas from onshore production wells and to compress and transport gas to a natural gas processing facility, transmission pipeline, or a distribution pipeline. In 2016, owners and operators began collecting information on this source category to report the combined emissions for all gathering and boosting equipment that they own or operate within each hydrocarbon basin to EPA under Subpart W of the GHGRP. Emissions from stationary and portable fuel combustion equipment are reported under "Subpart W" of the GHGRP. Learn more about this source. |
| 6 | Natural gas processing plants separate natural gas liquids from produced natural gas. Some natural gas processing plants also fractionate natural gas liquids into one or more components. These facilities report emissions from gas processing under Subpart W of the GHGRP and emissions from fuel combustion under Subpart C. Learn more about emissions from this source. |
| 7 | A natural gas liquids fractionator separates bulk natural gas liquids into constituent products (i.e., ethane, propane, butane, isobutene, or pentanes plus) or mixtures of products. Natural gas liquids fractionators must report under Subpart NN of the GHGRP the quantity of CO2 that would be emitted if the natural gas liquids that they supply each year were combusted or oxidized. Some natural gas liquids fractionators are co-located with natural gas processing plants. Learn more about reported CO2 from this source. |
| 8 | Natural gas transmission compression means any stationary compressors that move natural gas from production fields, natural gas processing plants, or other transmission compressors through transmission pipelines to natural gas distribution pipelines, LNG storage facilities, or underground storage sites. These facilities report process emissions under Subpart W of the GHGRP and emissions from fuel combustion under Subpart C. Learn more about emissions from this source. |
| 9 | Underground natural gas storage means subsurface storage of natural gas in formations such as depleted gas or oil reservoirs and salt dome caverns. Facilities report emissions from natural gas handling under Subpart W of the GHGRP and emissions from fuel combustion under Subpart C. Learn more about emissions from this source. |
| 10 | Liquefied natural gas (LNG) storage means onshore LNG storage vessels located above ground and associated equipment. These facilities report emissions under Subpart W of the GHGRP and emissions from fuel combustion under Subpart C. Learn more about emissions from this source. |
| 11 | LNG import and export equipment. LNG import equipment means all onshore or offshore equipment that receives imported LNG via ocean transport, stores LNG and delivers the gas to a natural gas transmission or distribution system. LNG export equipment means all onshore or offshore equipment that receives, liquefies and stores natural gas and transfers the LNG into ocean transport vessels. Process emissions from this source are reported under Subpart W of the GHGRP and emissions from fuel combustion are reported under Subpart C. Learn more about emissions from this source. |
| 12 | Onshore natural gas transmission pipelines deliver gas from processing plants to local natural gas distribution systems, often passing through one or more compressor stations. In 2016, owners are operators began collecting information on this source category to report emissions from transmission pipeline blowdowns to EPA under subpart W of the GHGRP. Learn more about this source. |
| 13 | Large natural gas and petroleum users report emissions from the use of natural gas or petroleum products as a fuel or process feedstock under other applicable Subparts of the GHGRP (e.g., electricity generation [subpart D], hydrogen production [subpart P], petrochemical production [subpart X], stationary fuel combustion sources [subpart C], and other source categories). |
| 14 | Natural gas distribution. Local natural gas distribution companies report emissions caused by leaks from distribution pipelines, regulating equipment, and transfer stations; and emissions from stationary fuel combustion under Subpart W of the GHGRP. Learn more about emissions from this source. |
| 15 | Local distribution companies also report under subpart NN the quantity of CO2 that would be emitted if the natural gas supplied to their customers were completely combusted, released, or oxidized. LDCs report total gas quantities supplied to four classes of customers - electricity generation, industrial, commercial, and residential. Learn more about reported CO2 associated with natural gas supplied. |